The common causes of pipe corrosion include water quality (chemicals like chlorine, pH levels, hard water substances), pipe material age/type (galvanized steel, lead, copper, iron), environmental factors (soil conditions, humidity), and temperature swings. These factors lead to issues like pitting, scaling, and structural damage, impacting pipes' lifespan. Homeowners should be vigilant about potential corrosion, especially in areas with plumbing leaks or inadequate ventilation, as understanding water chemistry is crucial for prevention.
The Science Behind Pipe Corrosion: Unraveling the Homeowner’s Guide
Pipe corrosion is a common yet complex issue affecting plumbing systems worldwide. Understanding the science behind it is crucial for homeowners to ensure their properties remain safe and efficient. This article delves into the common causes of pipe corrosion, exploring environmental factors, water chemistry, and material choices that contribute to its development. By examining these aspects, we can uncover the significant effects of corrosion on plumbing and learn effective preventive measures to protect homes from this pervasive problem.
- Common Causes of Pipe Corrosion
- – Metal pipes and their environmental exposure
- – Water chemistry and its impact on corrosion rates
Common Causes of Pipe Corrosion

Pipe corrosion is a common problem for homeowners, often leading to costly repairs and disruptions in their homes. Understanding the common causes of pipe corrosion is essential for maintaining plumbing systems. One major cause is water quality; high levels of chlorine or other chemicals used to treat drinking water can accelerate corrosion inside pipes. Additionally, copper and iron pipes are particularly susceptible to oxidation when in contact with dirty water containing dissolved gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Another significant factor is pipe material and age. Older pipes, especially those made from galvanized steel or lead, have a higher risk of corrosion due to their composition and exposure to moisture. Even modern materials can corrode over time if not properly maintained. Environmental factors such as soil conditions and humidity levels also play a role; pipes buried in moist, acidic soils tend to corrode faster than those in drier environments.
– Metal pipes and their environmental exposure
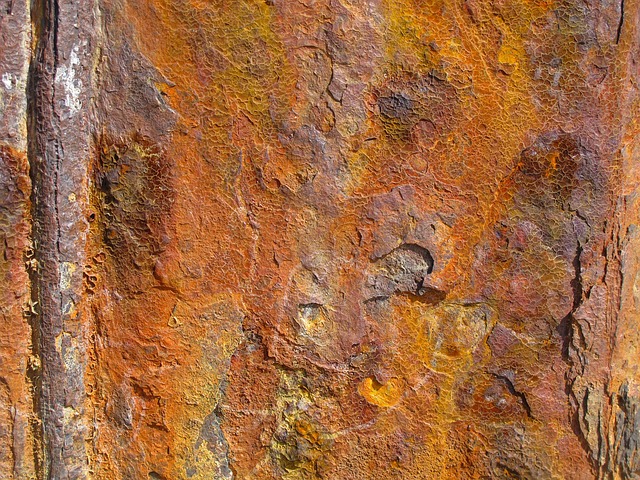
Metal pipes, particularly those used in plumbing systems, are susceptible to corrosion over time due to their constant exposure to various environmental factors. The science behind pipe corrosion is a complex interplay of chemical reactions and the material’s composition. In the case of metal pipes, the primary culprit is often water, which can contain dissolved minerals and gases that react with the pipe’s surface.
Common causes of pipe corrosion include moisture, temperature fluctuations, chemicals present in water (like chlorine), and exposure to corrosive substances like acid or salt. These factors can accelerate the deterioration process, leading to issues such as pitting, scaling, and eventual structural damage. Homeowners should be aware that even pipes hidden within walls or under floors are not immune to corrosion, especially if there’s a history of plumbing leaks or inadequate ventilation.
– Water chemistry and its impact on corrosion rates
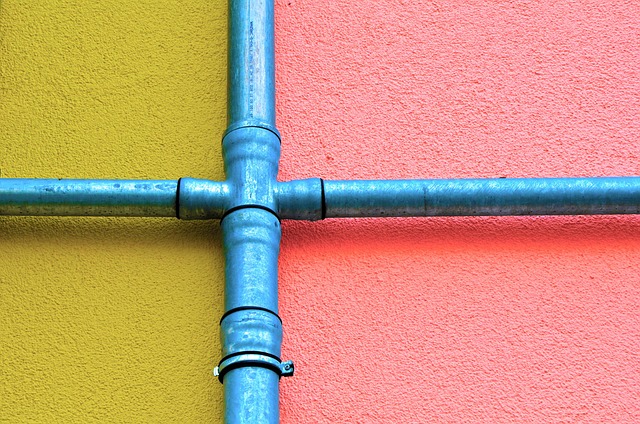
Water chemistry plays a significant role in determining the rate of pipe corrosion, one of the common causes of pipe degradation. The presence of certain substances in water can accelerate or inhibit corrosion. For instance, acidic water with low pH levels is highly corrosive and can swiftly damage pipes, especially metal ones. Conversely, water with high pH values, indicating alkalinity, may not be as aggressive but can still contribute to pipe deterioration over time.
The composition of water, including components like chlorine, calcium, magnesium, and various organic compounds, also influences corrosion rates. Hard water, rich in minerals, can lead to the formation of scale on pipes, which not only reduces their lifespan but also provides an environment conducive to corrosion. Understanding these chemical factors is crucial for homeowners to identify potential issues and implement preventive measures against pipe corrosion.
Understanding the science behind pipe corrosion is essential for homeowners to maintain their plumbing systems. By recognizing the common causes, such as metal pipes’ exposure to environmental elements and water chemistry’s role in accelerating corrosion rates, homeowners can take proactive measures. Regular inspection, proper maintenance, and utilizing corrosion-resistant materials are key strategies to prevent costly repairs and ensure the longevity of home plumbing infrastructure.
